Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Thyroid
- Subacute Thyroiditis in the Time of COVID-19
- Hwa Young Ahn
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):186-187. Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1928

- 758 View
- 39 Download

- Miscellaneous
- Incidence of Endocrine-Related Dysfunction in Patients Treated with New Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Meta-Analysis and Comprehensive Review
- Won Sang Yoo, Eu Jeong Ku, Eun Kyung Lee, Hwa Young Ahn
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):750-759. Published online November 13, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1785
- 1,442 View
- 121 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the incidence of endocrine immune-related adverse events (irAEs) for recently developed immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) drugs.
Methods
We collected studies on newly developed ICI drugs using PubMed/Medline, Embase, and Cochrane Library from inception through January 31, 2023. Among ICI drugs, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, and ipilimumab were excluded from the new ICI drugs because many papers on endocrine-related side effects have already been published.
Results
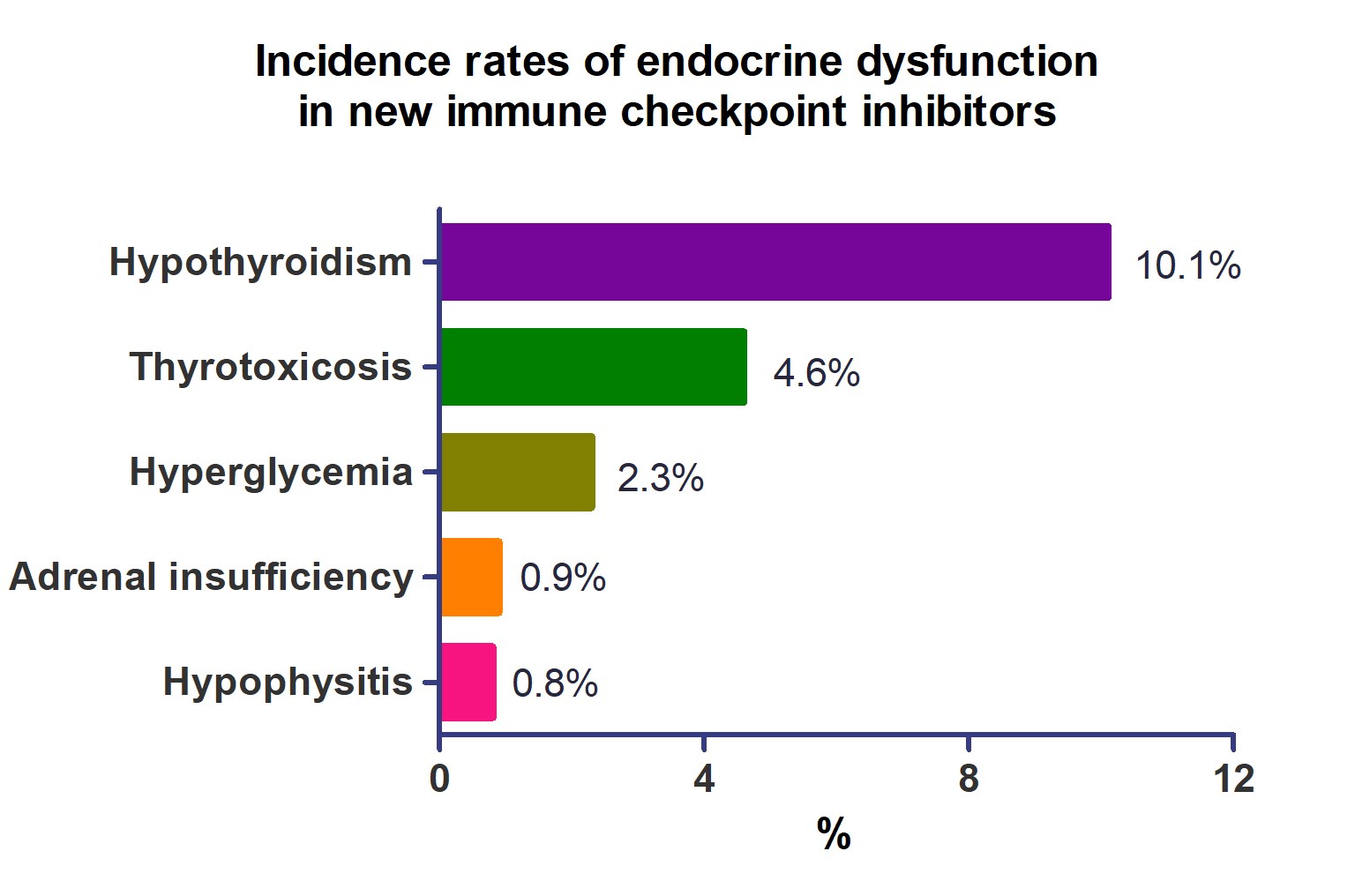
A total of 44,595 patients from 177 studies were included in this analysis. The incidence of hypothyroidism was 10.1% (95% confidence interval [CI], 8.9% to 11.4%), thyrotoxicosis was 4.6% (95% CI, 3.8% to 5.7%), hypophysitis was 0.8% (95% CI, 0.5% to 1.1%), adrenal insufficiency was 0.9% (95% CI, 0.7% to 1.1%), and hyperglycemia was 2.3% (95% CI, 1.6% to 3.4%). Hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis occurred most frequently with programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) inhibitors (13.7% and 7.5%, respectively). The rate of endocrine side effects for the combination of a programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitor (durvalumab) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 inhibitor (tremelimumab) was higher than that of monotherapy. In a meta-analysis, the combination of tremelimumab and durvalumab had a 9- to 10-fold higher risk of pituitary and adrenal-related side effects than durvalumab alone.
Conclusion
Newly developed PD-1 inhibitors had a high incidence of thyroid-related irAEs, and combined treatment with durvalumab and tremelimumab increased the risk of pituitary- and adrenal-related irAEs. Based on these facts, it is necessary to predict the endocrine side effects corresponding to each ICI drug, diagnose and treat them appropriately, and try to reduce the morbidity and mortality of patients.

- Thyroid
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Prevalence, Treatment Status, and Comorbidities of Hyperthyroidism in Korea from 2003 to 2018: A Nationwide Population Study
- Hwa Young Ahn, Sun Wook Cho, Mi Young Lee, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Hang-Seok Chang, Ka Hee Yi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):436-444. Published online July 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1684
- 1,806 View
- 127 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to investigate the changes of incidence and treatment of choice for hyperthyroidism from 2003 to 2018 and explore the treatment-related complications and concomitant comorbidities in South Korea using data from the National Health Insurance Service.
Methods
This is a retrospective observational study. Hyperthyroidism was defined as a case having two or more diagnostic codes of thyrotoxicosis, with antithyroid drug intake for more than 6 months.
Results
The average age-standardized incidence of hyperthyroidism from 2003 to 2018 was 42.23 and 105.13 per 100,000 men and women, respectively. In 2003 to 2004, hyperthyroidism was most often diagnosed in patients in their 50s, but in 2017 to 2018, people were most often diagnosed in their 60s. During the entire period, about 93.7% of hyperthyroidism patients were prescribed with antithyroid drugs, and meanwhile, the annual rates of ablation therapy decrease from 7.68% in 2008 to 4.56% in 2018. Antithyroid drug-related adverse events, mainly agranulocytosis and acute hepatitis, as well as complications of hyperthyroidism such as atrial fibrillation or flutter, osteoporosis, and fractures, occurred more often in younger patients.
Conclusion
In Korea, hyperthyroidism occurred about 2.5 times more in women than in men, and antithyroid drugs were most preferred as the first-line treatment. Compared to the general population, hyperthyroid patients may have a higher risk of atrial fibrillation or flutter, osteoporosis, and fractures at a younger age. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long-term effect of thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin on atrial fibrillation in euthyroid patients
Jung-Chi Hsu, Kang-Chih Fan, Ting-Chuan Wang, Shu-Lin Chuang, Ying-Ting Chao, Ting-Tse Lin, Kuan-Chih Huang, Lian-Yu Lin, Lung-Chun Lin
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Current Status of Hyperthyroidism in Korea
Hyemi Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 392. CrossRef - Is Thyroid Dysfunction Associated with Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms? A Population-Based, Nested Case–Control Study from Korea
Hyeree Park, Sun Wook Cho, Sung Ho Lee, Kangmin Kim, Hyun-Seung Kang, Jeong Eun Kim, Aesun Shin, Won-Sang Cho
Thyroid®.2023; 33(12): 1483. CrossRef
- Long-term effect of thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin on atrial fibrillation in euthyroid patients

- Thyroid
- Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Disease during Pregnancy and Postpartum: 2023 Revised Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines
- Hwa Young Ahn, Ka Hee Yi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(3):289-294. Published online June 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1696
- 6,498 View
- 706 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
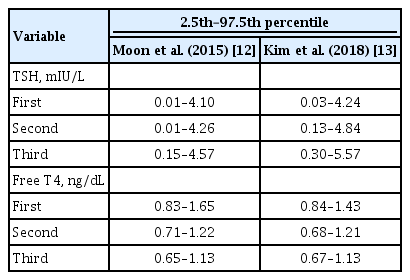
ePub - Thyroid hormone plays a critical role in fetal growth and development, and thyroid dysfunction during pregnancy is associated with several adverse outcomes, such as miscarriage and preterm birth. In this review, we introduce and explain three major changes in the revised Korean Thyroid Association (KTA) guidelines for the diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy: first, the normal range of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) during pregnancy; second, the treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism; and third, the management of euthyroid pregnant women with positive thyroid autoantibodies. The revised KTA guidelines adopt 4.0 mIU/L as the upper limit of TSH in the first trimester. A TSH level between 4.0 and 10.0 mIU/L, combined with free thyroxine (T4) within the normal range, is defined as subclinical hypothyroidism, and a TSH level over 10 mIU/L is defined as overt hypothyroidism regardless of the free T4 level. Levothyroxine treatment is recommended when the TSH level is higher than 4 mIU/L in subclinical hypothyroidism, regardless of thyroid peroxidase antibody positivity. However, thyroid hormone therapy to prevent miscarriage is not recommended in thyroid autoantibody-positive women with normal thyroid function.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Use of thyroid hormones in hypothyroid and euthyroid patients: A survey of members of the Endocrine Society of Australia
Nicole Lafontaine, Suzanne J. Brown, Petros Perros, Enrico Papini, Endre V. Nagy, Roberto Attanasio, Laszlo Hegedüs, John P. Walsh
Clinical Endocrinology.2024; 100(5): 477. CrossRef - Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Focus on Proven Health Effects in the 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines
Eu Jeong Ku, Won Sang Yoo, Hyun Kyung Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 381. CrossRef - Maternal isolated hypothyroxinemia in the first trimester is not associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes, except for macrosomia: a prospective cohort study in China
Jing Du, Linong Ji, Xiaomei Zhang, Ning Yuan, Jianbin Sun, Dan Zhao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Use of thyroid hormones in hypothyroid and euthyroid patients: A survey of members of the Endocrine Society of Australia

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
- Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):10-24. Published online February 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.102

- 3,739 View
- 262 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The Korean National Health Information Database (NHID) contains big data combining information obtained from the National Health Insurance Service and health examinations. Data are provided in the form of a cohort, and the NHID can be used to conduct longitudinal studies and research on rare diseases. Moreover, data on the cause and date of death are provided by Statistics Korea. Research and publications based on the NHID have increased explosively in the field of endocrine disorders. However, because the data were not collected for research purposes, studies using the NHID have limitations, particularly the need for the operational definition of diseases. In this review, we describe the characteristics of the Korean NHID, operational definitions of endocrine diseases used for research, and an overview of recent studies in endocrinology using the Korean NHID.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations Between Physical Activity and the Risk of Hip Fracture Depending on Glycemic Status: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Kyoung Min Kim, Kyoung Jin Kim, Kyungdo Han, Yumie Rhee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1194. CrossRef - Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
Jinyoung Kim, Bongseong Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 567. CrossRef - Diabetes severity and the risk of depression: A nationwide population-based study
Yunjung Cho, Bongsung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 351: 694. CrossRef - Information Bias Might Exaggerate Lung Cancer Risk of Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Nobuyuki Horita, Kaoru Takase-Minegishi
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2024; 19(2): 348. CrossRef - Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyu Na Lee, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes severity is strongly associated with the risk of active tuberculosis in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study with a 6-year follow-up
Ji Young Kang, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
Respiratory Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Research on obesity using the National Health Information Database: recent trends
Eun-Jung Rhee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(2): 35. CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef - Risk of Pancreatic Cancer and Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score-Matching Analysis
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soon Jib Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 426. CrossRef - Prevalence, Treatment Status, and Comorbidities of Hyperthyroidism in Korea from 2003 to 2018: A Nationwide Population Study
Hwa Young Ahn, Sun Wook Cho, Mi Young Lee, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Hang-Seok Chang, Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 436. CrossRef - Is Thyroid Dysfunction Associated with Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms? A Population-Based, Nested Case–Control Study from Korea
Hyeree Park, Sun Wook Cho, Sung Ho Lee, Kangmin Kim, Hyun-Seung Kang, Jeong Eun Kim, Aesun Shin, Won-Sang Cho
Thyroid®.2023; 33(12): 1483. CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - Risk of depression in patients with acromegaly in Korea (2006-2016): a nationwide population-based study
Shinje Moon, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
European Journal of Endocrinology.2023; 189(3): 363. CrossRef - Cumulative effect of impaired fasting glucose on the risk of dementia in middle-aged and elderly people: a nationwide cohort study
Jin Yu, Kyu-Na Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 770. CrossRef - Increased Risk of Hip Fracture in Patients with Acromegaly: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea
Jiwon Kim, Namki Hong, Jimi Choi, Ju Hyung Moon, Eui Hyun Kim, Eun Jig Lee, Sin Gon Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 690. CrossRef
- Associations Between Physical Activity and the Risk of Hip Fracture Depending on Glycemic Status: A Nationwide Cohort Study

- Thyroid
- Clinicopathological Characteristics and Recurrence-Free Survival of Rare Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas in Korea: A Retrospective Study
- Mijin Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Young Joo Park, Hwa Young Ahn, Hee Sung Kim, Yong Joon Suh, Dughyun Choi, Bu Kyung Kim, Go Eun Yang, Il-Seok Park, Ka Hee Yi, Chan Kwon Jung, Bo Hyun Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):619-627. Published online June 10, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.974
- 4,696 View
- 180 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to evaluate the clinicopathological features and biological behaviors of Korean thyroid cancer patients with rare variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) to address the ambiguity regarding the prognostic consequences of these variants.
Methods
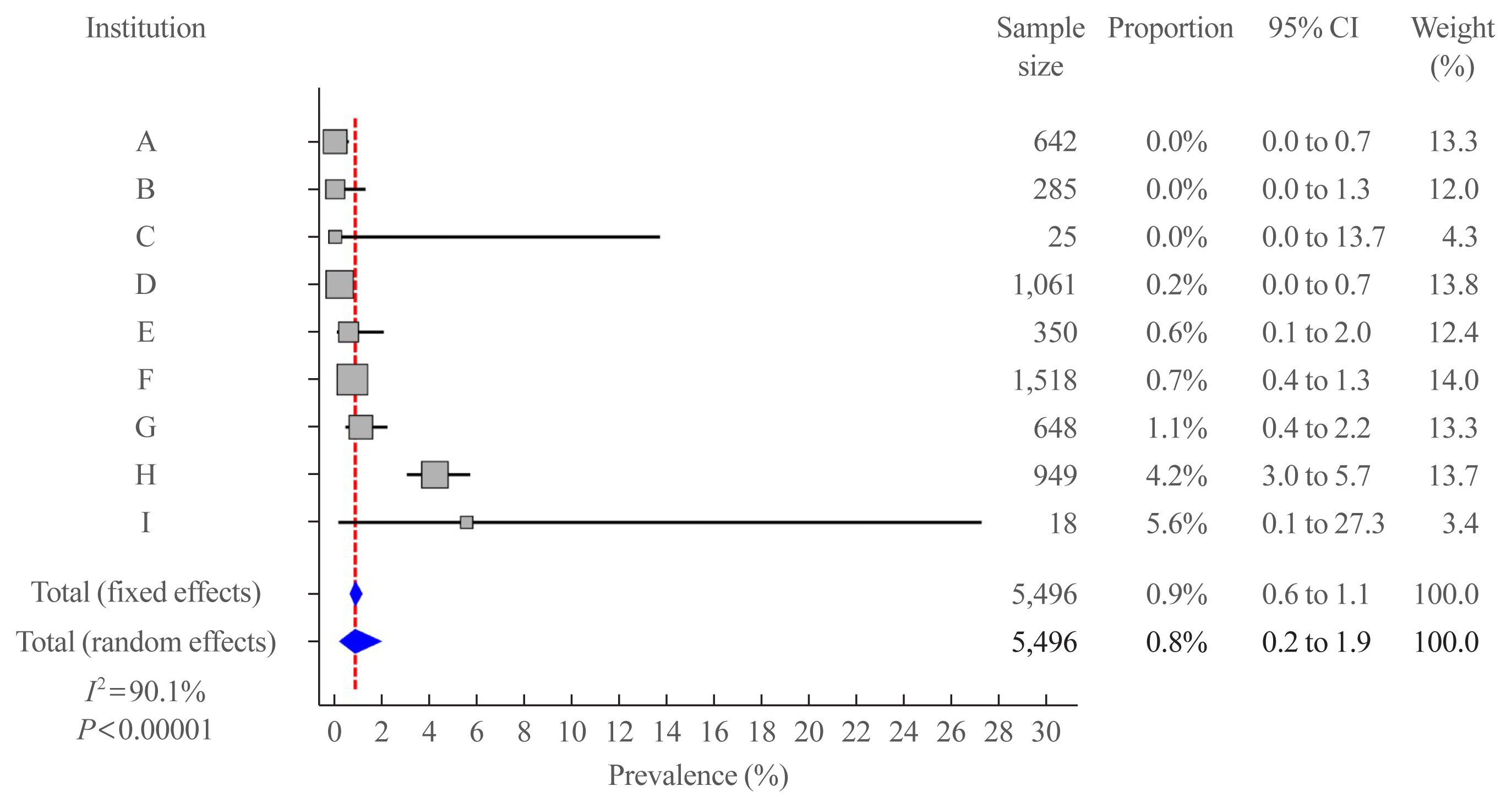
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 5,496 patients who underwent thyroid surgery for PTC, between January and December 2012, in nine tertiary hospitals. Rare PTC variants included tall cell (TCV), columnar cell (CCV), diffuse sclerosing (DSV), cribriform-morular (CMV), solid (SV), hobnail, and Warthin-like variants. Recurrence-free survival (RFS) was defined as the time from the date of thyroidectomy until recurrence.
Results
Rare variants accounted for 1.1% (n=63) of the PTC patients; with 0.9% TCV, 0.02% CCV, 0.1% DSV, 0.1% CMV, and 0.1% SV. The mean age of patients and primary tumor size were 42.1±13.1 years and 1.3±0.9 cm, respectively. Extrathyroidal extension and cervical lymph node metastasis were observed in 38 (60.3%) and 37 (58.7%) patients, respectively. Ultrasonographic findings revealed typical malignant features in most cases. During a median follow-up of 7 years, 6.3% of patients experienced a locoregional recurrence. The 5-year RFS rates were 71.4% in patients with DSV or SV, 95.9% for TCV, or CCV, and 100% for other variants. DSV emerged an independent risk factor associated with shorter RFS.
Conclusion
In this multicenter Korean cohort, rare variants accounted for 1.1% of all PTC cases, with TCV being the most frequent subtype. DSV emerged as a significant prognostic factor for RFS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Serum thyroglobulin testing after thyroid lobectomy in patients with 1–4 cm papillary thyroid carcinoma
Ahreum Jang, Meihua Jin, Chae A Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Endocrine.2023; 81(2): 290. CrossRef - Do Histologically Aggressive Subtypes of Papillary Thyroid
Microcarcinoma have Worse Clinical Outcome than Non-Aggressive Papillary Thyroid
Microcarcinoma Subtypes? A Multicenter Cohort Study
Sayid Shafi Zuhur, Hunkar Aggul, Ugur Avci, Selvinaz Erol, Mazhar Müslüm Tuna, Serhat Uysal, Gulhan Akbaba, Faruk Kilinç, Merve Catak, Sakin Tekin, Ogun Irem Bilen, Beyza Olcay Öztürk, Ecem Bilgehan Erden, Gulsah Elbuken, Halise Cinar Yavuz, Pinar Kadiogl
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(05): 323. CrossRef - The Warthin-like variant of papillary thyroid carcinomas: a clinicopathologic analysis report of two cases
Xing Zhao, Yijia Zhang, Pengyu Hao, Mingzhen Zhao, Xingbin Shen
Oncologie.2023; 25(5): 581. CrossRef - A Retrospective Cohort Study with Validation of Predictors of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Outcomes
Ayanthi Wijewardene, Anthony J. Gill, Matti Gild, Diana L. Learoyd, Anthony Robert Glover, Mark Sywak, Stan Sidhu, Paul Roach, Geoffrey Schembri, Jeremy Hoang, Bruce Robinson, Lyndal Tacon, Roderick Clifton-Bligh
Thyroid.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological Implications of the BRAFV600E Mutation in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma of Ukrainian Patients Exposed to the Chernobyl Radiation in Childhood: A Study for 30 Years After the Accident
Liudmyla Zurnadzhy, Tetiana Bogdanova, Tatiana I. Rogounovitch, Masahiro Ito, Mykola Tronko, Shunichi Yamashita, Norisato Mitsutake, Michael Bolgov, Serhii Chernyshov, Sergii Masiuk, Vladimir A. Saenko
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Serum thyroglobulin testing after thyroid lobectomy in patients with 1–4 cm papillary thyroid carcinoma

- Clinical Study
- Trends in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma in Korea
- Hwa Young Ahn, Jae Eun Chae, Hyemi Moon, Junghyun Noh, Young Joo Park, Sin Gon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):811-819. Published online November 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.709

- 6,189 View
- 192 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Thyroid cancer is becoming increasingly common worldwide, but little is known about the epidemiology of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC). This study investigated the current status of the incidence and treatment of MTC using Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) data for the entire Korean population from 2004 to 2016.
Methods
This study included 1,790 MTC patients identified from the NHIS database.
Results
The age-standardized incidence rate showed a slightly decreasing or stationary trend during the period, from 0.25 per 100,000 persons in 2004 to 0.19 in 2016. The average proportion of MTC among all thyroid cancers was 0.5%. For initial surgical treatment, 65.4% of patients underwent total thyroidectomy. After surgery, external-beam radiation therapy (EBRT) was performed in 10% of patients, a proportion that increased from 6.7% in 2004 to 11.0% in 2016. Reoperations were performed in 2.7% of patients (n=49) at a median of 1.9 years of follow-up (interquartile range, 1.2 to 3.4). Since November 2015, 25 (1.4%) patients with MTC were prescribed vandetanib by December 2016.
Conclusion
The incidence of MTC decreased slightly with time, and the proportion of patients who underwent total thyroidectomy was about 65%. EBRT, reoperation, and tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy are additional treatments after initial surgery for advanced MTC in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Update on C-Cell Neuroendocrine Neoplasm: Prognostic and Predictive Histopathologic and Molecular Features of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Chan Kwon Jung, Shipra Agarwal, Jen-Fan Hang, Dong-Jun Lim, Andrey Bychkov, Ozgur Mete
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(1): 1. CrossRef - Mouse Models to Examine Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Pathogenesis: Recent Updates
Hye Choi, Kwangsoon Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(13): 11138. CrossRef - Partial preservation of the normal thyroid gland based on tumor diameter may be possible in small medullary thyroid carcinoma: a two-center 15-year retrospective study
Guiming Fu, Xiaoyi Li, Fengli Guo, Xianhui Ruan, Wei Zhang, Weijing Zhang, Yaping Zhang, Yibo Chen, Chunhua Li, Jin Chen, Xiangqian Zheng, Zhaohui Wang, Ming Gao
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Socioeconomic Status With Long-Term Outcome in Survivors After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: Nationwide Population-Based Longitudinal Study
Kyung Hun Yoo, Yongil Cho, Jaehoon Oh, Juncheol Lee, Byuk Sung Ko, Hyunggoo Kang, Tae Ho Lim, Sang Hwan Lee
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e47156. CrossRef - Preoperative identification of low-risk medullary thyroid carcinoma: potential application to reduce total thyroidectomy
Hyunju Park, Hyun Jin Ryu, Jung Heo, Man Ki Chung, Young Ik Son, Jung-Han Kim, Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Young Lyun Oh, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Jee Soo Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics, Surgical Management, and Prognostic Factors of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Retrospective, Single-Center Study
Xin Wu, Binglu Li, Chaoji Zheng
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2022; 21: 153303382210784. CrossRef - Understanding and Utilizing Claim Data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) and Health Insurance Review & Assessment (HIRA) Database for Research
Dae-Sung Kyoung, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(2): 103. CrossRef - Unilateral Surgery for Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Seeking for Clinical Practice Guidelines
Daqi Zhang, Carla Colombo, Hui Sun, Hoon Yub Kim, Antonella Pino, Simone De Leo, Giacomo Gazzano, Luca Persani, Gianlorenzo Dionigi, Laura Fugazzola
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Total thyroidectomy vs thyroid lobectomy for localized medullary thyroid cancer in adults: A propensity-matched survival analysis
Weili Liang, Jinyuan Shi, Hui Zhang, Guixu Lv, Tiantian Wang, Yong Wang, Bin Lv, Luchuan Li, Qingdong Zeng, Lei Sheng
Surgery.2022; 172(5): 1385. CrossRef - Constitutive Cytomorphologic Features of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Using Different Staining Methods
Chih-Yi Liu, Chien-Chin Chen, Andrey Bychkov, Shipra Agarwal, Yun Zhu, Jen-Fan Hang, Chiung-Ru Lai, Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park, Weiwei Li, Zhiyan Liu, Deepali Jain, Ayana Suzuki, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Noel Chia, Min En Nga, Tikamporn Jitpasutham, Somboon K
Diagnostics.2021; 11(8): 1396. CrossRef - Metastatic Lymph Node Ratio for Predicting Recurrence in Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Jinyoung Kim, Jun Park, Hyunju Park, Min Sun Choi, Hye Won Jang, Tae Hyuk Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
Cancers.2021; 13(22): 5842. CrossRef - A High Frequency of Lobectomy Instead of Total Thyroidectomy to Treat Medullary Thyroid Cancer in Korea: Data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service
Sun Wook Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 784. CrossRef
- Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database

- Miscellaneous
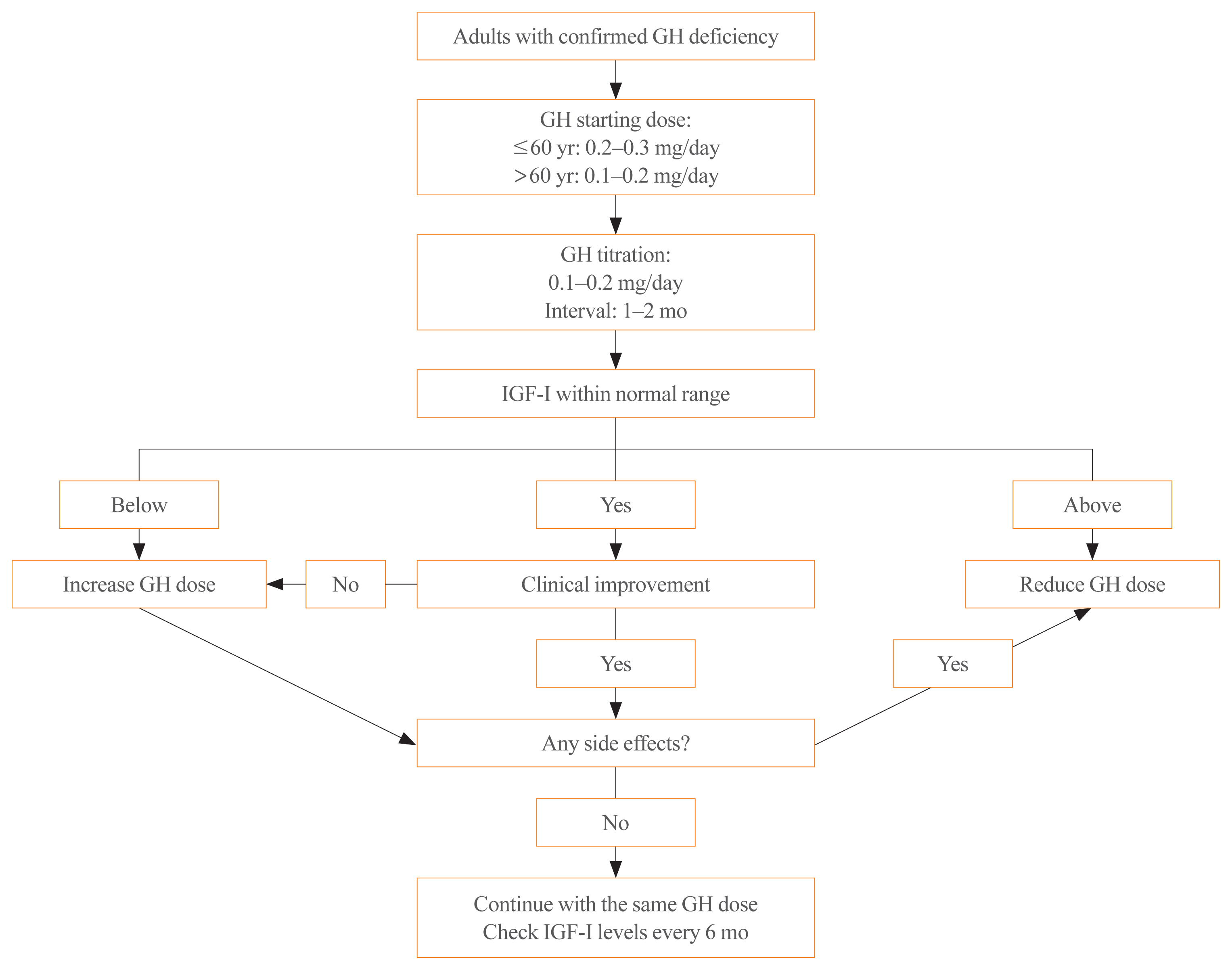
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Growth Hormone Deficiency: A Position Statement from Korean Endocrine Society and Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology
- Jung Hee Kim, Hyun Wook Chae, Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyeong Hye Park, Dong Jun Lim, Kwang Joon Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Gyuri Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Seong Hee Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Yul Hwangbo, Ju Hee Lee, Bu Kyung Kim, Yong Jun Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Hwa Young Ahn, Hoon Sung Choi, Sang Mo Hong, Dong Yeob Shin, Ji A Seo, Se Hwa Kim, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Hoon Yu, Byung Joon Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Sung-Woon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Eun Jig Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):272-287. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.272
- 9,477 View
- 428 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Growth hormone (GH) deficiency is caused by congenital or acquired causes and occurs in childhood or adulthood. GH replacement therapy brings benefits to body composition, exercise capacity, skeletal health, cardiovascular outcomes, and quality of life. Before initiating GH replacement, GH deficiency should be confirmed through proper stimulation tests, and in cases with proven genetic causes or structural lesions, repeated GH stimulation testing is not necessary. The dosing regimen of GH replacement therapy should be individualized, with the goal of minimizing side effects and maximizing clinical improvements. The Korean Endocrine Society and the Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology have developed a position statement on the diagnosis and treatment of GH deficiency. This position statement is based on a systematic review of evidence and expert opinions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial
Ghina Tsurayya, Cut Alifiya Nazhifah, Muhammad Rahmat Pirwanja, Putri Oktaviani Zulfa, Muhammad Raihan Ramadhan Tatroman, Fajar Fakri, Muhammad Iqhrammullah
Children.2024; 11(2): 227. CrossRef - Evaluation of Adult Height in Patients with Non-Permanent Idiopathic GH Deficiency
Agnese Murianni, Anna Lussu, Chiara Guzzetti, Anastasia Ibba, Letizia Casula, Mariacarolina Salerno, Marco Cappa, Sandro Loche
Endocrines.2023; 4(1): 169. CrossRef - The effect of hypothalamic involvement and growth hormone treatment on cardiovascular risk factors during the transition period in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung-Eun Cheon, Choong Ho Shin, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(2): 107. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Possible Aid for Detecting Hypoglycemic Events during Insulin Tolerance Tests
Soo Yeun Sim, Moon Bae Ahn
Sensors.2023; 23(15): 6892. CrossRef - The risk patients with AGHD have of developing CVD
Eisha Javed, Maha Zehra, Naz Elahi
International Journal of Cardiology Cardiovascular Risk and Prevention.2023; 19: 200221. CrossRef - Diagnosis of GH Deficiency Without GH Stimulation Tests
Anastasia Ibba, Sandro Loche
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Impacts of Discontinuation and Resumption of Recombinant Human Growth Hormone Treatment during the Transition Period in Patients with Childhood-Onset Growth Hormone Deficiency
Yun Jeong Lee, Yunha Choi, Han-Wook Yoo, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Han Saem Choi, Ho-Seong Kim, Jae Hyun Kim, Jung Eun Moon, Cheol Woo Ko, Moon Bae Ahn, Byung-Kyu Suh, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 359. CrossRef - A Radiomics-Based Model with the Potential to Differentiate Growth Hormone Deficiency and Idiopathic Short Stature on Sella MRI
Taeyoun Lee, Kyungchul Song, Beomseok Sohn, Jihwan Eom, Sung Soo Ahn, Ho-Seong Kim, Seung-Koo Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2022; 63(9): 856. CrossRef - Phenotypic spectrum of patients with mutations in CHD7: clinical implications of endocrinological findings
Ja Hye Kim, Yunha Choi, Soojin Hwang, Gu-Hwan Kim, Han-Wook Yoo, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrine Connections.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Endocrine Disorders: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Hyemi Kwon, Eun Roh, Chang Ho Ahn, Hee Kyung Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 839. CrossRef - Laron syndrome: clinic, diagnostics (а clinical case)
P.M. Lіashuk, R.P. Lіashuk, N.I. Stankova, M.B. Kudina
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2022; 18(3): 193. CrossRef - Diagnosis for Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Joint Position Statement of the Korean Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma Task Force
Eu Jeong Ku, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Chang Ho Ahn, Kyung Ae Lee, Seung Hun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Kyeong Hye Park, Yun Mi Choi, Namki Hong, A Ram Hong, Sang-Wook Kang, Byung Kwan Park, Moon-Woo Seong, Myungshin Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Chan
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 322. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation Guidelines for Adrenal Tumor Ablation
Byung Kwan Park, Masashi Fujimori, Shu-Huei Shen, Uei Pua
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 553. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation guidelines for renal cell carcinoma
Byung Kwan Park, Shu-Huei Shen, Masashi Fujimori, Yi Wang
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2021; 62(4): 378. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency
Jung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2021; 96(5): 400. CrossRef
- Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial

- Endocrine Research
- Thyroid Hormone Regulates the mRNA Expression of Small Heterodimer Partner through Liver Receptor Homolog-1
- Hwa Young Ahn, Hwan Hee Kim, Ye An Kim, Min Kim, Jung Hun Ohn, Sung Soo Chung, Yoon-Kwang Lee, Do Joon Park, Kyong Soo Park, David D. Moore, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(4):584-592. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.584
- 3,764 View
- 39 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Expression of hepatic cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) is negatively regulated by orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner (SHP). In this study, we aimed to find whether thyroid hormone regulates SHP expression by modulating the transcriptional activities of liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1).
Methods We injected thyroid hormone (triiodothyronine, T3) to C57BL/6J wild type. RNA was isolated from mouse liver and used for microarray analysis and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Human hepatoma cell and primary hepatocytes from mouse liver were used to confirm the effect of T3
in vitro . Promoter assay and electrophoretic mobility-shift assay (EMSA) were also performed using human hepatoma cell lineResults Initial microarray results indicated that SHP expression is markedly decreased in livers of T3 treated mice. We confirmed that T3 repressed SHP expression in the liver of mice as well as in mouse primary hepatocytes and human hepatoma cells by real-time PCR analysis. LRH-1 increased the promoter activity of SHP; however, this increased activity was markedly decreased after thyroid hormone receptor β/retinoid X receptor α/T3 administration. EMSA revealed that T3 inhibits specific LRH-1 DNA binding.
Conclusion We found that thyroid hormone regulates the expression of SHP mRNA through interference with the transcription factor, LRH-1.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bile acid and receptors: biology and drug discovery for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Ting-ying Jiao, Yuan-di Ma, Xiao-zhen Guo, Yun-fei Ye, Cen Xie
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2022; 43(5): 1103. CrossRef - Loperamide induces excessive accumulation of bile acids in the liver of mice with different diets
Zili Lei, Hedong Rong, Yanhong Yang, Siping Yu, Tianle Zhang, Lei Chen, Ya Nie, Qi Song, Qing Hu, Jiao Guo
Toxicology.2022; 477: 153278. CrossRef - Pathogenesis of hypothyroidism-induced NAFLD is driven by intra- and extrahepatic mechanisms
Giuseppe Ferrandino, Rachel R. Kaspari, Olga Spadaro, Andrea Reyna-Neyra, Rachel J. Perry, Rebecca Cardone, Richard G. Kibbey, Gerald I. Shulman, Vishwa Deep Dixit, Nancy Carrasco
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Bile acid and receptors: biology and drug discovery for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease

- Thyroid
- Letter: The Biochemical Prognostic Factors of Subclinical Hypothyroidism (Endocrinol Metab 2014;29:154-62, Myung Won Lee et al.)
- Hwa Young Ahn, Yun Jae Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(3):400-401. Published online September 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.3.400
- 2,924 View
- 26 Download

- A Case of Ectopic ACTH Syndrome Associated with Metastatic Prostate Cancer.
- Eun Ky Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Hwa Young Ahn, Ah Reum Khang, Hyo Jin Park, So Yeon Park, Sang Eun Lee, Hak Chul Jang, Seong Yeon Kim, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(3):237-243. Published online September 19, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.3.237
- 1,801 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) syndrome is mostly associated with neuroendocrine tumors and small cell carcinoma of the lung. This syndrome of prostate cancer is rare and has been reported in only a few cases. We report a patient with ectopic ACTH production associated with metastatic prostate cancer. A 70-year-old patient with metastatic prostate cancer was admitted to our hospital with septic shock. He had a history of hormonal therapy and transurethral prostatectomy. Adrenocortical function was checked due to consistent fever and poor general condition, which revealed markedly increased levels of basal plasma ACTH and serum cortisol. The patient did not present typical signs of the Cushing's syndrome, however, hypokalemia and a history of hypertension were found. He died in days as a result of multi-organ failure. On pathology, the prostatectomy specimen showed a tumor composed of mixed populations of adenocarcinoma and small cell carcinoma. The tumor cells in the small cell component were positive for chromogranin and ACTH. Although neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer is rare, etopic ACTH production should be considered in patients with prostate cancer as well as in clinical features of ACTH hypersecretion.

- Effect of Thyroid Hormone to the Expression of Bile Salt Export Pump.
- Hwa Young Ahn, Kwan Jae Lee, Soon Hui Kim, Eun Ky Kim, Ah Reum Kang, Jung Ah Lim, Ji Won Yoon, Kyung Won Kim, Do Joon Park, Bo Youn Cho, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(3):232-238. Published online September 1, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.3.232
- 66,074 View
- 27 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Bile acids were important for the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Thyroid hormone increased the expression of CYP7A1 (cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase), catalyzing the first step in the biosynthesis of bile acids. However, the effect of thyroid hormone on bile acid export has not been previously assessed. The principal objective of this study is to evaluate the effects of thyroid hormone on the bile salt export pump (BSEP). METHODS: Thyroid hormone, T3 (1 mg/g) was administered to male mice via intraperitoneal injection. After 6 hours and 5 days of T3 treatment, we measured serum total and LDL cholesterol and hepatobiliary bile acid concentrations. We assessed the changes associated with bile acid synthesis and transport. In order to evaluate the direct effect of thyroid hormone, we assessed the changes in the levels of BSEP protein after T3 administration in human hepatoma cells. RESULTS: Serum total and LDL cholesterol were reduced and hepatobiliary bile acid concentrations were increased following T3 treatment. Expressions of Cyp7a1 and BSEP mRNA were increased following T3 treatment. The levels of the BSEP protein in the mouse liver as well as in the human hepatoma cells were increased after T3 treatment. CONCLUSION: Thyroid hormone can regulate LDL cholesterol metabolism. It increases bile acid synthesis and the excretion of bile acids via increased BSEP expression. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hypothyroidism Increases Cholesterol Gallstone Prevalence in Mice by Elevated Hydrophobicity of Primary Bile Acids
Irina Kube, Luca Bartolomeo Tardio, Ute Hofmann, Ahmed Ghallab, Jan G. Hengstler, Dagmar Führer, Denise Zwanziger
Thyroid.2021; 31(6): 973. CrossRef - Thyroid Dysfunction and Cholesterol Gallstone Disease
Irina Kube, Denise Zwanziger
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2020; 128(06/07): 455. CrossRef - Thyroid hormone receptor β1 stimulates ABCB4 to increase biliary phosphatidylcholine excretion in mice
Julien Gautherot, Thierry Claudel, Frans Cuperus, Claudia Daniela Fuchs, Thomas Falguières, Michael Trauner
Journal of Lipid Research.2018; 59(9): 1610. CrossRef
- Hypothyroidism Increases Cholesterol Gallstone Prevalence in Mice by Elevated Hydrophobicity of Primary Bile Acids

- A Case of Acute Suppurative Thyroiditis in a Patient with Leukemia Who was Treated with Chemotherapy.
- Hoon Sung Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Jae Seok Lee, Hyosang Kim, Jung Ah Lim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Minjoo Kim, Yenna Lee, Do Jun Park, Bo Youn Cho
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(1):38-41. Published online March 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.1.38
- 2,091 View
- 21 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Acute suppurative thyroiditis (AST) is a rare disease of the thyroid gland that results from anatomical abnormalities, such as pyriform sinus fistula. However, in some case reports, patients with AST did not have anatomical abnormalities, including a report in which children with acute leukemia developed AST after chemotherapy. We report a case of AST in an adult with a hematologic disorder treated with chemotherapy. Although he was initially treated with parenteral antibiotics, surgical intervention was performed due to progressive worsening of AST. He recovered after surgical intervention and had no anatomical abnormality.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Infection of Thyroid Cyst Occurring 1 Month after Fine-Needle Aspiration in an Immunocompetent Patient
Jung Kyu Park, Eon Ju Jeon
International Journal of Thyroidology.2018; 11(2): 182. CrossRef - A Case of Acute Suppurative Thyroiditis with Thyrotoxicosis in an Elderly Patient
Bo Sang Kim, Kil Woo Nam, Jeong Eun Kim, Ji Hoon Park, Jun Sik Yoon, Jung Hwan Park, Sang Mo Hong, Chang Bum Lee, Yong Soo Park, Woong Hwan Choi, You Hern Ahn, Dong Sun Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2013; 28(1): 50. CrossRef
- Infection of Thyroid Cyst Occurring 1 Month after Fine-Needle Aspiration in an Immunocompetent Patient

- Discrepancy between the Growth Hormone and Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Concentrations in Patients with Acromegaly.
- Ji Won Yoon, Mi Yeon Kang, Hwa Young Ahn, Jee Hyun An, Sang Wan Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Seong Yeon Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(6):395-403. Published online December 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.6.395
- 1,864 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
This study was performed to evaluate the frequency and clinical characteristics of patients with active acromegaly and who show discordance of the growth hormone (GH) level and the insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) level. METHODS: We reviewed the medical records of the patients who were diagnosed with acromegaly between 01/01/1995 and 6/30/2007 at Seoul National University Hospital. We selected only the patients whose basal GH and IGF-I levels were available. We investigated the pre- and post-operative clinical characteristics, as well as the blood concentrations of GH and IGF-I. The concordance rate between the two hormones was examined. The patients were considered to have active disease on the basis of their IGF-I levels above the normal range, after adjustment for age and gender, and their mean basal GH value was > or = 2.5 microgram/L. The hormone levels and the clinical parameters were compared between the hormone concordant and discordant groups. RESULTS: We reviewed the preoperative records of 103 acromegalic patients, and these patients met the above-mentioned criteria. 53 postoperative patients who were not cured by operation were monitored without them receiving radiation or medical therapy. Both the basal GH and IGF-I levels were above normal in 103 patients preoperatively, and the discordant rate was 0% (0/103 cases). Postoperatively, the discordant rate between the two hormones was increased to 30.2% (16/53 cases). Age, gender, body mass index and tumor size were insignificantly different between the concordant and discordant groups. However, postoperative residual tumors were less frequently observed in the discordant group (P = 0.006). CONCLUSION: For the patients with acromegaly, unlike the 0% discordance preoperatively, 30.2% of patients showed a discrepancy between their GH and IGF-I levels postoperatively. The patients who had hormonal discrepancy were less likely to have residual tumors after operation. Considering the frequency of this hormonal discrepancy, both hormone levels should be measured to evaluate the disease activity after treatment. Further, oral glucose tolerance testing should be performed and especially for the patients with an increased GH level, but who have a normal IGF-I concentration.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



